Useful information to start
Here you can consult the necessary procedures to create a company, register as a self-employed person or the telematic constitution of limited companies. For online processing, we put at your disposal the PAE (Entrepreneurship Service Points) of the Single Window for Entrepreneurs and the Madrid Emprende network of business incubators.
- Guide 01 Limited Companies I – Incorporation procedures (PDF)
- Guide 02 Limited Companies II – Beginning of activity (PDF)
- Guide 03 Capitalization of unemployment (PDF)
- Guide 04 Individual entrepreneur – Activity start procedures (PDF)
- Guide 05 Electronic incorporation of companies (PDF)
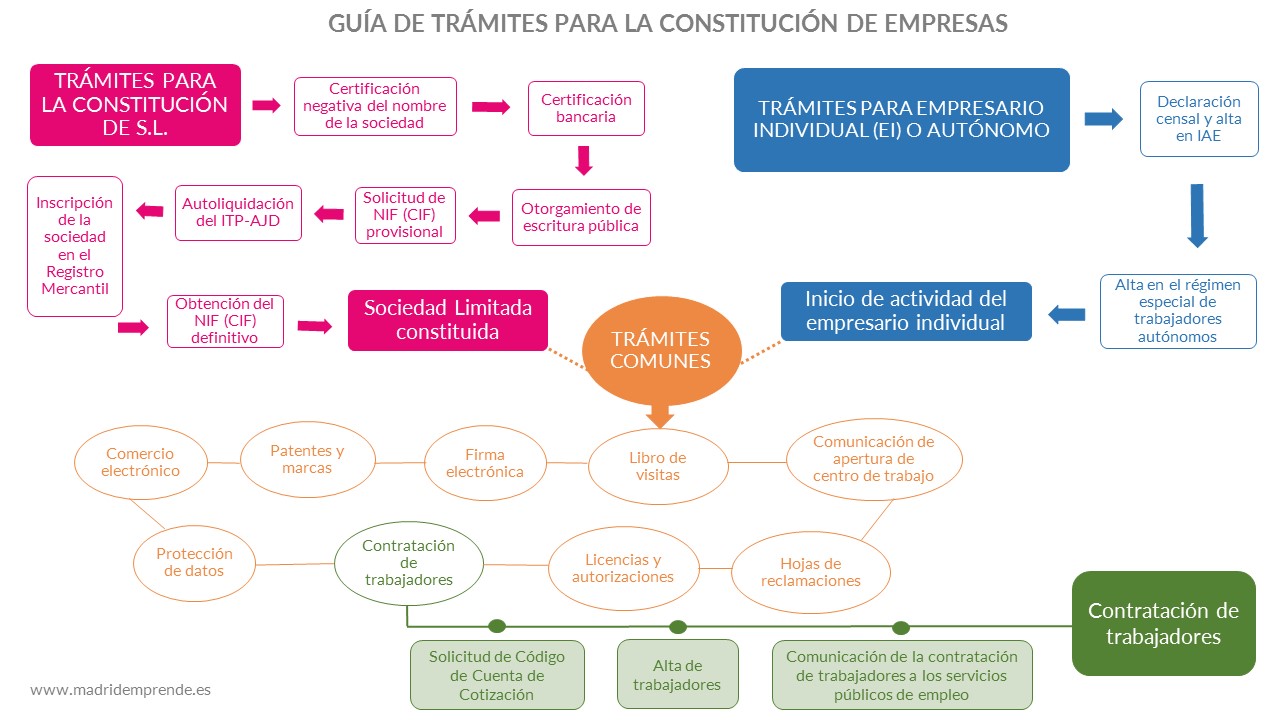
We offer you a list of resources and useful elements to start and create your company.
Law creates and grows
We offer you a abstract of Law 18/22, of September 28, on the creation and growth of companies.
business plan
- Manual for the development of the business plan. Basic guide for the preparation of the business plan that the Madrid City Council makes available to entrepreneurs. It is complemented with the Simulator.
- Business plan simulator. Complementary tool to the Business Plan Manual for you to enter your project data and obtain the final document in pdf format.
- Tool to prepare the business plan. Tool developed by the DGIPYME that helps to develop the online business plan. Requires registration.
Taxation
- Taxation and accounting for businessmen and professionals, individuals physical. This document prepared by the Tax Agency details all the tax obligations that businessmen and professionals, natural persons, have to comply with.
- Guide to the new Accounting Plan for SMEs. Guide prepared by the Ministry of Industry, Tourism and Commerce, for the application of the PGC PYME, which tries to simplify and systematize the information, incorporating examples and exercises, on the basis of the Regulations approved in Royal Decree 151. Modified and updated BOE no. January 26, 30, 2021
- Taxpayer Calendar 2023. Prepared by the Tax Agency, aimed at reminding compliance with the main state tax obligations.
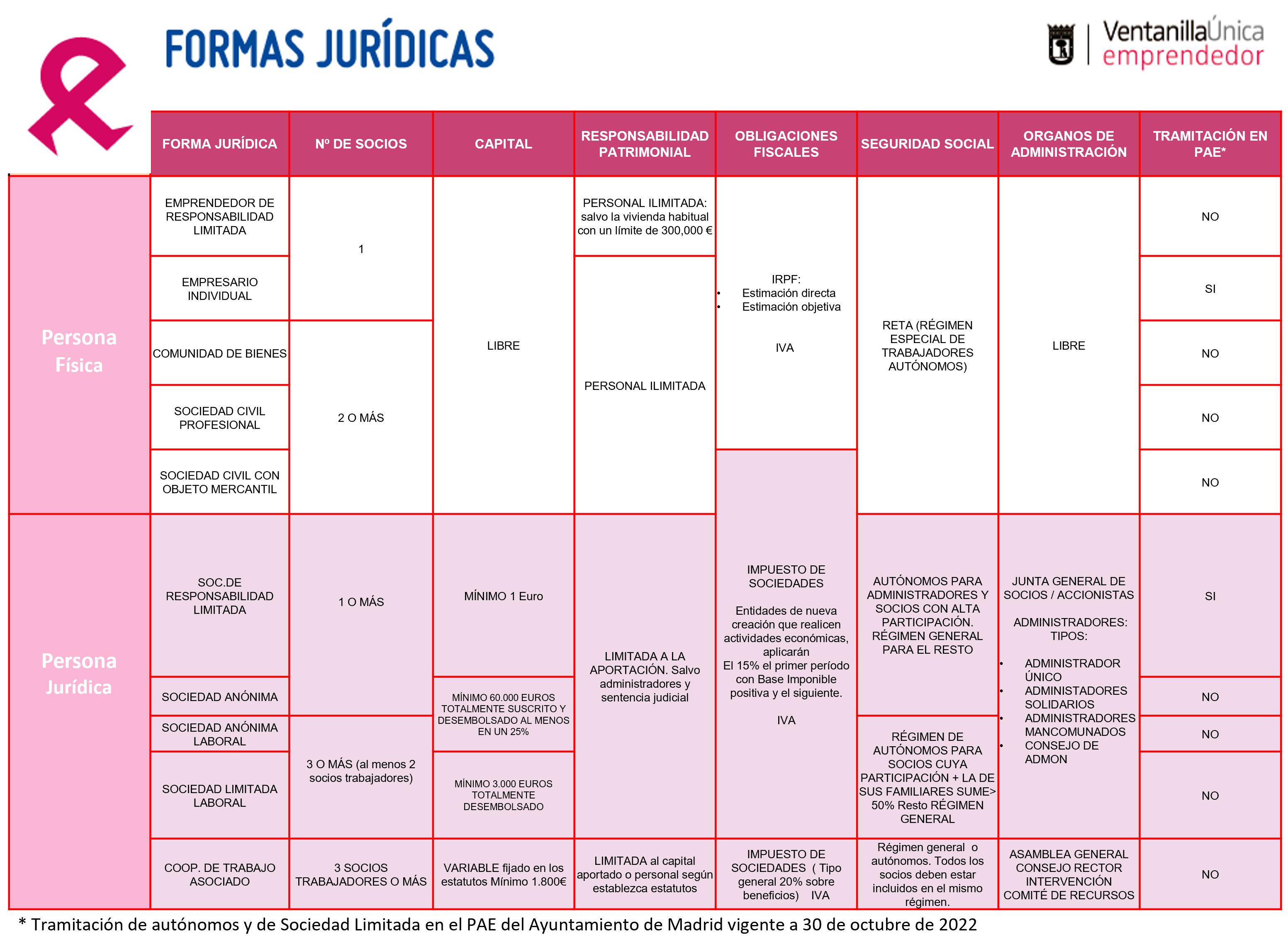
Creation / dissolution of companies
- Choice of legal form. Help tool when choosing the legal form for the company.
- Creation of companies. Business creation processes and flowcharts according to the chosen legal form (DGIPYME).
- Limited companies I – Incorporation procedures. Informative triptych on the necessary procedures for the creation of a Limited Company.
- Limited companies II – Beginning of activity. Informative brochure that exposes the most common procedures for the start-up and development of the activity.
- Individual entrepreneur – Procedures to start activity. Informative brochure that details the mandatory procedures necessary to register as self-employed.
- Telematic incorporation of companies. Informs about the electronic processing of SL and the documents necessary to carry it out.
- Capitalization of unemployment. It is an aid that allows you to convert the amount of the unemployment benefit pending receipt into a single payment.
- Company: termination of the company. Manual published by the DGIPYME.
- Company: extinction of the company. Manual published by the DGIPYME.
- termination of self-employment. Manual published by the DGIPYME.
Other links of interest
- Tax agency
- Chamber of Madrid
- Entrepreneurs Portal – Madrid Community
- Spanish office of the patents and brand
- European SME Portal
Social economy:
Here you will find information on some of the grants and subsidies that may be of interest.
Aid for self-employed workers, entrepreneurs and social economy entities
- Aid for the promotion of CSR and work-life balance
- Aid to workers who are self-employed
- Extension of the flat rate for freelancers
- Program for the promotion of collective entrepreneurship
- Single payment of the contributory benefit
- Help for the payment of Social Security contributions, after capitalizing the unemployment benefit
More information: Portal of the Community of Madrid
Innovation Check Program of the Community of Madrid
It is about facilitating the access of small and medium-sized companies to technology and innovation, through the direct granting of aid, in the form of subsidies, aimed at SMEs and, with special preference, those belonging to non-traditional sectors. commercial, financial or real estate and whose business model is not based on the generation or development of technological innovations. Thus, it is about promoting the implementation of innovation and the transfer of scientific and technological knowledge by small and medium-sized companies, as an added value and as an instrument for increasing their productivity.
More information in the next link: Innovation Check Program
Dynamic aid and incentive guide
Complete and updated guide to grants and incentives with an open application period
This guide from the General Directorate for Industry and Small and Medium Enterprises includes all the aid and incentives for companies, granted and called by the general administration of the State, regional administrations, local administrations and other public bodies.
More information: Dynamic Guides and SME platform
The help portal offers the following services:
Venues for entrepreneurs
If you are an entrepreneur and you are looking for a place to develop your business project or activity, the Social Housing Agency of the Community of Madrid makes available to Madrid entrepreneurs, an offer of premises for lease, under very advantageous conditions.
Here you have all the information about the premises for entrepreneurs: characteristics, location, rental advantages…..
Support in the search for financing
In addition to aid and subsidies for SMEs and the self-employed in Madrid, various financial institutions have financing lines for entrepreneurial projects
More links of interest
- Search engine for grants and incentives for companies
- Grants and incentives for business creation
- Entrepreneurship: portal of the Community of Madrid
- Subsidies and incentives for hiring the Community of Madrid
- Contract guide. Public State Employment Service (SEPE)
- Guide types of Sepe 2023 contracts
- Grants from the Community of Madrid
- Grants from the Community of Madrid
Microbank social microcredits
With the aim of promoting self-employment and encouraging entrepreneurial activity, the Madrid City Council has signed an agreement with the financial institution Microbank to support access to financing for the establishment, consolidation or expansion of micro-enterprises, self-employed businesses and self-employment projects .
In addition, especially, a financing line is established aimed at business projects of an innovative nature.
To access these lines of financing it is necessary to provide a business plan and get a favorable feasibility report of the project prepared by Madrid Emprende, as a MicroBank collaborating entity.
Interested entrepreneurs can contact us requesting appointment.
For more information consult the conditions in micro bank
Other financing lines
ICO Companies and Entrepreneurs Lines
What does it finance?
- Investment projects, business activities and/or need for liquidity or expenses.
- Digitization projects and, in particular, those aimed at promoting teleworking solutions included in the program Accelerate SMEs.
- Rehabilitation of houses and buildings.
For whom?
- For freelancers and entrepreneurs.
- Individuals and communities of owners.
More information and other possible lines of financing at: www.ico.es

ENISA lines
ENISA actively participates in the financing of business projects feasible and innovative. Have 5 lines:
- Young Entrepreneurs. Aimed at young entrepreneurs who want to create companies. Objective: to provide the necessary financial resources to recently established SMEs, created by young people, so that they can undertake the investments required by the project in its initial phase.
- Entrepreneurs. Aimed at entrepreneurs who want to create companies with a clear competitive advantage. Objective: to financially support SMEs promoted by entrepreneurs, without age limits, in the early stages of life, so that they undertake the necessary investments and carry out their project.
- Increase. Aimed at supporting the business projects of companies interested in expanding their business or achieving competitive improvement.
- AgroInnpulse. Aimed at promoting the digital transformation of companies in the agri-food sector and the rural environment.
- Digital Entrepreneurss. Aimed at promoting female digital entrepreneurship.

avalmadrid
Financing for SMEs and the self-employed.
Investment:

The Business Angels or private investor are natural persons with extensive knowledge of certain sectors and with investment capacity, who promote the development of business projects with high growth potential in its early stages of life, providing capital and added value to management.
Private investors help cover the lack of financing faced by entrepreneurs in the early stages (associated with high levels of risk and lack of liquidity); they differ from traditional investors and venture capital, in their involvement in the management of the company.
Like venture capital entities, these are investors who are committed to a business project, without getting involved in the day-to-day, but providing added value. In addition to capital availability, these private investors tend to have a high level of knowledge in the sectors in which they invest. This knowledge, its management capacity and its network of contacts are very valuable for promoting the development of business projects that have high growth potential, in exchange for medium-term profitability.
As a legal form, they usually adopt that of a limited company. These investors usually organize themselves by forming networks. In some cases with the aim of converting in others as a form of cooperation in general.
Main features:
- They invest their own money
- It is invested in the initial stage of the life of a company
- Your investment decisions may be other than strictly financial motivations (job satisfaction, etc.)
- They invest in areas close to their place of residence
- The amounts invested are much lower than the average dedicated by venture capital entities in each operation
- Profitability is generally lower than that obtained by venture capital entities
Main networks operating in Madrid
- Network of Private Investors and Family Offices. The objective of the Network is to facilitate contact between entrepreneurs in search of financing and investors in search of investment opportunities.
- Business Angels Network madri+d. Network specialized in technological projects of the Community of Madrid during its first years of life.
- Keiretsu Forum. The largest international network of private investors. In Spain it is promoted above all by the Caixa, the EOI and the Chambers of Commerce.
- IE Business School entrepreneurship. The Venture Days is IE's investment forum. It is quite focused on the best projects of the students or members of the business school.
- Spanish Association of Business Angels Networks. It brings together 25 of the main Spanish networks.
The Innovative SME Seal is created by virtue of the Order ECC/1087/2015, of June 5, which regulates obtaining the Small and Medium-sized Innovative Company seal and creates and regulates the Registry of Small and Medium-sized Innovative Companies (BOE of June 11, 2015).
It is a recognition that is granted to small and medium-sized companies that have a great character innovative so that these SMEs can take advantage of and combine tax incentives which, without this seal, are incompatible.
The objective is the development of an environment favorable to the R&D in SMEs so that innovation is systematically incorporated into the production model of our SMEs.
This new certification aims to expand the bonuses and tax benefits to these small and medium-sized companies, as well as to bring them closer to public procurement more easily.
How to get the stamp?
The application for the Seal can be made by SMEs that are in any of the following circumstances:
- Have received public funding in the last 3 years (without revocation) through:
- Public calls for the VI National Plan for Scientific Research, Development and Technological Innovation or the State Plan for Scientific and Technical Research and Innovation.
- Grants for carrying out CDTI R&D projects
- Aid from the 7th R&D&I Framework Program or the Horizon 2020 Program of the European Union.
- Having demonstrated its innovative character with its activity:
- Because it has its own patent in exploitation for less than 5 years
- Because you have obtained in the last 3 years a Motivated Binding Report or IMV favorable
- Have demonstrated their capacity for innovation with one of these certifications:
- Young Innovative Company (JEI), (AENOR EA0043)
- Innovative small or micro-enterprise, (AENOR EA0047)
- R&D&i management systems, (UNE 166.002 Standard)
A Registry is created in which all innovative SMEs will be recorded. Registration will be carried out at the request of the interested SME, carrying out the procedures electronically. These are: declaration as SME; not having had total revocation of justified public financial aid; be up to date with the Administration (Treasury and SS) and justification of the condition of innovator.
Advantages: what is the seal for?
With the Seal, SMEs can obtain better tax advantages for their investment in R&D&i, such as:
- Match incentives that are not compatible for the rest of the companies:
- Bonuses to Social Security by Research staff: reduces by 40% the share of common Social Security contingencies for researchers on staff.
- Tax deductions for R+D+i: that allow reducing the Corporation Tax up to 42% of the investment made in R&D and up to 12% of the investment made in Technological Innovation (IT).
- Do use of the Seal for advertising and commercial purposes, since it improves the image of the brand
- Access to certain aid, financing or mechanisms for which the seal is necessary, such as participation in tenders for Public Purchase of Innovation, or the ICO financing facility.
How to get the Innovative SME Seal
The registration request as it is done from the website of the Ministry of Innovation, electronically and free of charge. The company must be registered in the RUS (Unified Registry of Applicants) to start the application for the seal.
During the application process we will be asked for information:
- Company data
- Data of the applicant
- Company information: number of employees, turnover, annual balance
- Provide the document that proves that you are an Innovative SME, as we have seen in the requirements section, for example:
- documentation on the granting of public aid
- the own patent in exploitation
- a copy of the resolution of the positive binding reasoned report
- or the copy of the official certification recognized by the Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness
- Electronic signature
Then we must wait for the resolution of the Ministry, which can take from a week to 4 months. If you do not get any response within this time, it is most likely that your request has been accepted and you can now download the stamp.
The Seal expires at 3 years and you can renew it as long as you continue to meet the requirements.
SME Accelerate Plan
Given the situation we are experiencing due to COVID-19, many companies are having to adapt their work by establishing alternative remote working mechanisms so as not to stop their activity.
Teleworking is a great challenge for many companies, which is why the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Digital Transformation will launch a financing program for the corresponding material by activating aid and credits for SMEs within the program Accelerate SMEs of the public company red.es, in order to articulate a set of initiatives in collaboration with the private sector to support SMEs in the short and medium term.
How can this plan help you if you are an SME that has had to adapt your work to teleworking due to COVID-19?
The Accelerate SMEs plan provides support to speed up the digitization process of your company, offering different resources to SMEs that range from advice to training. Specific:
- Creation of an information channel of resources for digitization, and specifically for the application of teleworking solutions, through the portal Accelerate SMEs
- Expansion of offices of the Digital Transformation Offices program and improvement of personalized advice and support services for SMEs.
- Launch of the Accelerate SME – Talent program to reinforce training.
- Support for the creation of technological solutions for the digitization of SMEs: line of aid to promote R&D&I business leadership of Spanish digital companies.
- Financial support for digitization, through ICO lines for the purchase and leasing of equipment and services for digitization and teleworking solutions. Companies will be provided with financing of up to 200 million euros through the Official Credit Institute (ICO) to meet the financial needs of SMEs in their activities and investments, for the purchase and leasing of equipment and services for digitization, among others, and, in particular, for the provision of work solutions no presential.
MORE INFORMATION:
Royal Decree Law 8/2020 of March 17
This information is indicative, not binding in any case. It is conceived as information to support entrepreneurship. It is recommended to check the official regulations and, where appropriate, study and consult each specific case.
